Given a rectangular cake with height h and width w, and two arrays of integers
horizontalCuts and verticalCuts where horizontalCuts[i] is the distance
from the top of the rectangular cake to the i-th horizontal cut and similarly,
verticalCuts[j] is the distance from the left of the rectangular cake to the
j-th vertical cut.
Return the maximum area of a piece of cake after you cut at each horizontal and
vertical position provided in the arrays horizontalCuts and verticalCuts.
Since the answer can be a huge number, return this modulo .
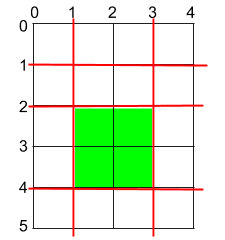
Example 1
- Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [1, 2, 4], verticalCuts = [1, 3]
- Output: 4
- Explanation: The figure represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green piece of cake has the maximum area.
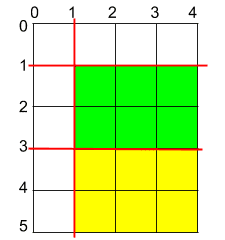
Example 2
- Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3,1], verticalCuts = [1]
- Output: 6
- Explanation: The figure represents the given rectangular cake. Red lines are the horizontal and vertical cuts. After you cut the cake, the green and yellow pieces of cake have the maximum area.
Example 3
- Input: h = 5, w = 4, horizontalCuts = [3], verticalCuts = [3]
- Output: 9
Approach: Sorting
Analysis
As seen in the figure above each horizontal cut cuts all the vertical cuts and form rectangles. Thus, the maximum area (cross-section) of the rectangle would be formed by maximum gap between horizontal cuts and vertical cuts.
To find the consecutive gaps, we need to first sort horizontalCuts and verticalCuts. In the following implementation, getMaxGap
is used to find the maximum gap between the cuts (horizontal and vertical).
- First,
we sort the
cutsarray and then assignmaxGaptocuts[0](difference between start and first cut). - We then iterate through the array and find the maximum gap between subsequent cuts.
- Finally, we calculate the gap between last cut and end, and if it is greater
than
maxGap, we assignmaxGapto this value.
getMaxGap is called for both horizontalCuts and verticalCuts, and we find
the maximum area by multiplying the returned results.
Implementation
In C++:
int getMaxGap(vector<int> &cuts, int length) {
sort(cuts.begin(), cuts.end());
// gap between start (0) and first cut
int maxGap = cuts[0];
for (int i = 1; i < (int)cuts.size(); ++i) {
// gap between subsequent cuts
maxGap = max(maxGap, cuts[i] - cuts[i - 1]);
}
// gap between last cut and end
maxGap = max(maxGap, length - cuts.back());
return maxGap;
}
int maxArea(int h, int w, vector<int>& horizontalCuts, vector<int>& verticalCuts) {
const int mod = 1'000'000'007;
const int x = getMaxGap(horizontalCuts, h);
const int y = getMaxGap(verticalCuts, w);
return (int)((long) x % mod * (long) y % mod) % mod;
}In Python:
def getMaxGap(cuts, length):
cuts.sort()
# gap between start (0) and first cut
maxGap = cuts[0]
for i in range(1, len(cuts)):
# gap between subsequent cuts
maxGap = max(maxGap, cuts[i] - cuts[i - 1])
# gap between last cut and end
maxGap = max(maxGap, length - cuts[-1])
return maxGap
def maxArea(h, w, horizontalCuts, verticalCuts):
mod = 10**9 + 7
x = getMaxGap(horizontalCuts, h)
y = getMaxGap(verticalCuts, w)
return (x % mod * y % mod) % modComplexity Analysis
- Time Complexity: required for sorting (where len(horizontalCuts), len(verticalCuts))
- Space Complexity: , constant space required